Internet Speed Test | Jitter Speed Test -
What is jitter speed test?
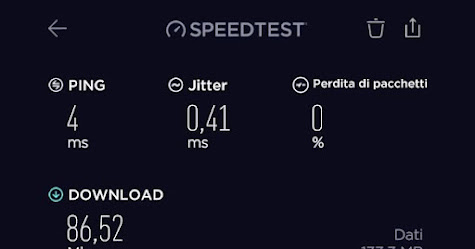
Jitter speed test is a measurement used to assess the stability and consistency of an internet connection. Jitter refers to the variation in the delay of data packets as they travel from one point to another over a network. It can affect the quality of real-time communication applications such as VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) and video conferencing.
During a jitter speed test, a series of data packets is sent from the testing server to the client device and then returned back to the server. The test measures the differences in the delay times between the packets' departure and arrival. The results are typically presented as the average jitter value, which indicates the average variation in the delay.
Jitter is usually measured in milliseconds (ms), and lower values are desirable. A high jitter value can cause audio or video disruptions during real-time communication, leading to poor call quality and video lag.
Jitter speed tests are often performed alongside other network performance tests such as ping and download/upload speed tests to get a comprehensive understanding of the overall network quality and reliability. Several online tools and applications are available that can conduct jitter speed tests to help diagnose and troubleshoot network issues.
What is kbs?
"Kbs" is an abbreviation commonly used to represent kilobits per second, a unit of measurement for data transfer rate or bandwidth. It is often used to describe the speed at which data is transmitted or received over a network.
In computer networking and telecommunications, data transfer rates are typically expressed in bits per second (bps) or their multiples. Here are some common units used to measure data transfer rates:
1 kilobit per second (Kbps) = 1,000 bits per second
1 megabit per second (Mbps) = 1,000,000 bits per second
1 gigabit per second (Gbps) = 1,000,000,000 bits per second
Note that kilobits per second (Kbps) should not be confused with kilobytes per second (KB/s). The latter refers to the data transfer rate in bytes, where 1 byte is equal to 8 bits. Therefore, 1 kilobyte per second (KB/s) is equal to 8 kilobits per second (Kbps).
When discussing internet speeds or network bandwidth, you will often encounter terms like "10 Mbps" (megabits per second) or "1000 Mbps" (gigabits per second) to indicate the speed of data transmission.
What is mbps?
Mbps" stands for megabits per second. It is a unit of measurement used to express the data transfer rate or bandwidth of a network connection. Mbps indicates how many millions of bits can be transmitted or received per second.
Bits are the smallest unit of digital information and are used to measure data transfer rates. A megabit (Mb) is equal to one million bits. When we refer to a network speed of, for example, 100 Mbps, it means that data can be transmitted or received at a rate of 100 million bits per second.
Mbps is commonly used to describe internet connection speeds, indicating the rate at which data can be downloaded or uploaded. Higher Mbps values generally indicate faster internet speeds and better data transmission capabilities. However, it's important to note that the actual speeds experienced by users can be affected by various factors, including network congestion, distance from the network source, and the capabilities of the devices being used.
It's worth mentioning that Mbps should not be confused with megabytes per second (MB/s), which is a unit of measurement for data storage or file sizes. To convert Mbps to MB/s, you divide the Mbps value by 8, as there are 8 bits in a byte. For example, a 100 Mbps connection would have a transfer speed of approximately 12.5 MB/s (100 Mbps ÷ 8 = 12.5 MB/s).